Sets of genes or HP condition lists are very useful for tracking
complex data-mining sequences of analysis. For example, derived named
gene sets may be used in successive data filters and for reports. For
example, one could do the following experiment given four different
types of HPs for (e.g. virgin, pregnancy, lactation, and
involution)
| First compare two HPs using a statistical test such as a t-test. Then save the resulting set of genes under the name "virgin vs. pregnancy". Then compare the next two HPs and save the resulting genes under the name "lactation vs. involution". Finally, compute the difference of genes found in "virgin vs. pregnancy" that are not found in "lactation vs. involution". This resulting gene set could then be saved (e.g. with a name "Genes found in virgin vs. pregnancy, but not in lactation vs. involution"). Similarly, taking the intersection of these two named sets shows genes that are common between the two sets. Taking the union shows genes found in either of the two named sets. |
The Edit menu contains the following main selections. All of these entities and preferences are saved as part of the startup state when you do a (File | Databases | SaveAs ... DB).
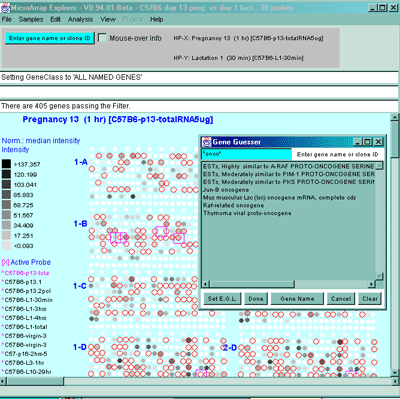
Figure 2.3.1 Edited Gene List defined from the Gene Name Guesser
using wildcards. The Edited Gene List was defined as the set of
genes containing the sub-string "onco" in it. The sub-string was
specified to the popup guesser window as "*onco*" using '*' characters
as wildcard symbols indicating that it should match any or no
characters. The button Gene Name may be toggled through a set
of other identifiers including Clone ID, UniGene ID, dbEST 3', dbEST
5', GenBank 3', and GenBank 5', LocusID, etc. depending on what
identifiers are available in your database. The user then pressed the
Set E.G.L. button on the guesser window that sets the E.G.L. to
those genes. If you have enabled the View menu "Show 'edited gene
list', then the genes in the EGL. are viewed as magenta squares seen
in the pseudoarray image. You many to do additional editing to
manually add or remove genes that you want to change in the set. If a
2D scatter plot was being used, EGL labeled genes would appear there
as well. To select a particular gene as the current gene, click on the
gene you want in the list, then press the Done button.
If you are running MAExplorer in stand-alone mode, the current named
gene sets are saved when you save the DB using the Save disk DB
or Save as disk DB selections in the Databases submenu of the
File menu. The gene sets are saved in a State sub directory as
".cbs" files and are used to restore the gene sets when restarting
MAExplorer on a .mae startup file. The .mae startup file saves the
names of the .cbs files that are shared among the various startup
files for a given project. The implication then is that if you change
and save a gene set in one startup database, it will change in other
startup databases when they load that gene set. The advantage is that
different startup databases may view a gene set produced by another
database.
The Sets of genes operations in the Edit menu include:
The following is an example of List saved gene sets state
listing the catalog of named gene subsets in some of the MGAP
data. Note that sets #1 to #11 are fixed by the data in the GIPO file
and may not be changed by the user. Sets #12 to #14 are assignable
from other sets or in the case of the E.G.L, by various MAExplorer
operations. Sets #1 through #14 may not be removed whereas #15 and
higher may be removed.
The following figure illustrates selecting sets by name for gene set
operations.
Figure 2.3.2 Selection of gene sets for binary gene set
operations. This example computes the Boolean AND of two sets "ALL
NAMED GENES" and "60 genes closest to CA-III from Named and Ests", and
then the AND of the "Replicates" with the previous result. The first
result is save in the set called "The 60 genes closest to Carbonic
Anhydrase-III". The second result is saved in the called set "Named
genes in the 60 genes closest to CA-III". Finally, the third result
is saved in the set named "Replicate genes in the 60 genes closes to
CA-III".
The following is an example of List saved HP condition lists
state listing the catalog of named HP condition lists.
The following is an example of List contents of saved HP condition
list state.
The Font Family submenu is used to set
the text font family. This may be useful if your computer is missing
some fonts or some fonts are easier to read than others. Note: some
fonts may not work well on your computer. If this is the case, try
another font. When you save the data mining session with the "SaveAs
file DB", it also saves the font you have set. For some plots or popup
text-windows, you may have to regenerate the popup window to see the
font changes.
Figure 2.3.4.1 Popup window allowing you to adjust all threshold
slider values">. The Adjust all Filter threshold scrollers
command allows you to pre-adjust all threshold slider values used in
data filtering and in clustering. It may be easier to set the
approximate range before invoking the clustering operation because
changing a parameter will recluster your data.
The Define HP-X (HP-Y) class name command may be used to change
the names of the HP-X (HP-Y) experimental condition sets. These names
are used in various labels in the main window, popup plots and
reports, etc. The commands to change various names of database
components are in the Preferences submenu in the Edit menu.
2.3.1 User edited gene list - the 'Edited Gene List' menu
You may define and edit arbitrary sets of genes using the User
edited gene list submenu to modify the 'Edited Gene List'
(EGL). This has sub-modes of operation for adding or removing genes
from the image by clicking on spots. If the Show 'Edited Gene
List' mode is set, you may see exactly which genes you have
defined by the magenta squares drawn around each gene in the EGL. Many
of the clustering operations will leave the current cluster in the
EGL. The commands include:
This gives you the functionality of adding and deleting genes from a
user defined list of genes to be analyzed. The EGL may be used with
the gene-set operations discussed in Section
2.3.2. You may also define genes in the EGL using the "Gene Name
Guesser" shown in Figure 2.3.1.![]() Show 'Edited Gene List' [CB] - toggle showing the EGL as
magenta boxes in the pseudoarray image. If enabled, genes set by
manual selection or as the result of some filtering operations
Show 'Edited Gene List' [CB] - toggle showing the EGL as
magenta boxes in the pseudoarray image. If enabled, genes set by
manual selection or as the result of some filtering operations
![]() Don't edit [RB] - clicking on a spot does nothing
(i.e. disable the 'click to add (remove) genes to (from) the E.G.L.'.
Don't edit [RB] - clicking on a spot does nothing
(i.e. disable the 'click to add (remove) genes to (from) the E.G.L.'.
![]() Click to add gene to E.G.L. (Ctrl/click) [RB] -
clicking on a spot adds the corresponding gene to the 'Edited
Gene List'.
Click to add gene to E.G.L. (Ctrl/click) [RB] -
clicking on a spot adds the corresponding gene to the 'Edited
Gene List'.
![]() Click to remove gene from E.G.L. (Shift/click) [RB] -
clicking on a spot removes the corresponding gene from the
'Edited Gene List'.
Click to remove gene from E.G.L. (Shift/click) [RB] -
clicking on a spot removes the corresponding gene from the
'Edited Gene List'.
2.3.2 Sets of genes menu
These commands let you do comparisons of sets of genes generated under
different criteria. In addition, you may compute derived gene sets
from existing gene sets using set operations (OR, AND,
DIFFERENCE). You may also normalize the data by a gene subset. The
user may save the genes defined by: 1) by the Filter, or 2) the
manually defined 'Edited Gene List'. The gene set resulting
from a binary gene set operation OR (union), AND (intersection), or
DIFFERENCE are saved in a new named gene set. The set difference (A-B) is
defined as the gets in set A that are not in set B. Genes in set B
that are not in set A are ignored. The 'User Filter Gene Set' may be
set to any gene set and may then be used as part of the gene Filter
cascade. The 'User Normalization Gene Set' may be set to any gene set
and may then be used to normalize gene intensity values across
hybridized samples. (See normalization
algorithm for more information on this method.)
User Gene Sets
Set# |#genes| title
=======================
#1 |1727| ALL GENES
#2 |394| ALL NAMED GENES
#3 |246| ESTs similar to genes
#4 |456| ESTs
#5 |1096| All genes and ESTs
#6 |1681| Good genes
#7 |40| Replicate genes
#8 |0| HousekeepingGenes
#9 |96| Calibration DNA
#10 |77| Your plates
#11 |46| Empty wells
--------- User Assignable ----------
#12 |0| User Filter Gene Set
#13 |60| Edited Gene List
#14 |0| Normalization Gene Set
--------- User definable------------
#15 |60| The 60 genes closest to Carbonic Anhydrase-III
#16 |30| Named genes in the 60 genes closest to CA-III
#17 |4| Replicate genes in the 60 genes closes to CA-III

2.3.3 Sets of sample conditions menu
In addition, MAExplorer can operate on sets of hybridized samples. For
example, a sample set might be replicate hybridized samples from the
same biological experiment sample, or it could be repeated experiments
of different but the same types of samples. (One must be careful in
mixing data between the two cases because of the different expected
sources of variance). This means you can treat multiple replicate
samples as a distribution and compare the mean values for each gene in
one set of samples with the mean values for another set of samples. We
call these sets of hybridized samples conditions lists or HP
lists. You may then put one or more HP samples into a condition
set. These sets in turn can be used for computing statistics on
clonal differences between different condition sets. Note each
condition set may have multiple (i.e. different) samples. These
condition sets are saved with the user state when doing a
(File | Databases | SaveAs DB). As with sets of genes, there are a
number of operations to manipulate HP condition set in the Sets of
Conditions menu that includes:
Condition Lists
===============
Condition[1] #HPs 2, [Initial HP-X: C57B6 pregnancy day 13]
Condition[2] #HPs 2, [Initial HP-Y: Stat5a (-,-) pregnancy day 13]
Condition[3] #HPs 4, [Initial HP-E expression list]
Condition List #1 [Initial HP-X: C57B6 pregnancy day 13]
====================================
HP[1] Pregnancy 13 (1 hr) [C57B6-p13-totalRNA5ug]
HP[2] Pregnancy 13 (1 hr) [C57B6-p13.2poly-A]
2.3.4 Setting user preferences menu
The Preferences submenu is used to set various data labels,
statistical limits and other parameters. These include:
![]() #Use Web DB [CB] - if Web DB was defined, get data from the Web
#Use Web DB [CB] - if Web DB was defined, get data from the Web
![]() #Web DB data caching [CB] - if Web DB was defined, cache data
on local computer if getting data from the Web
#Web DB data caching [CB] - if Web DB was defined, cache data
on local computer if getting data from the Web
![]() Cluster on Filtered genes, else all genes [CB] -
genes to use when clustering from current gene [Future]
Cluster on Filtered genes, else all genes [CB] -
genes to use when clustering from current gene [Future]


